Surface Ice Spectra
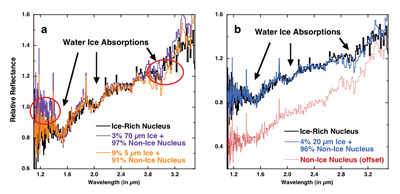
Modelling IR spectra of non-ice regions of the nucleus combined with water ice at various particle sizes.
a) The ice-rich nucleus spectrum (black), when modeled as a mixture of non-ice nucleus (see Fig. 4b) and a calculated spectrum of 70 µm size water ice particles (purple) does not match at short wavelengths, while a mixture with 3 µm size water ice particles (orange) produces a poor match at long wavelengths.
b) The same ice-rich spectrum (black) is well modeled with 30 µm size water ice particles (blue) and a nearby non-ice nucleus spectrum (red; offset by ?0.3 for clarity). Modeling indicates that the ice-regions contain 6 ± 3% of ice with 30 ± 20 µm size particles.
In her article "Exposed Water Ice Deposits on the Surface of Comet Tempel 1," Dr. Jessica Sunshine et al. goes into detail about the detection of these water ice deposits.
CREDIT: NASA/UM/SAIC J. M. Sunshine et al., Science 311, 1453 (2006); published online 2 February 2006 (10.1126/science.1123632). Reprinted with permission from AAAS. Permission to reproduce.











